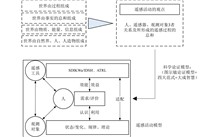
Modeling approach is one of the key means of expressing and understanding of remote sensing activities. The remote sensing activity model set discussed herein is with the recognition of the interplay among remote sensing systems, observation targets, and individuals. It is formulated through several layers, of simplification and standardization, across dimensions including information, data, hardware and software, as well as evaluation. The systems engineering approach, derived from the integration of this suite of remote sensing activity models, robustly applied in several projects demonstration, exploring the role of remote sensing systems in practical construction and application, continuously enhancing their maturity, and providing strong support for establishing a system characterized by "Chinese standards, Chinese data, Chinese technology, and Chinese applications" featuring independent innovation.
As a pivotal pillar of China's aerospace industry, aerospace remote sensing technology exerts a profound and far-reaching influence on the development level and overall competitiveness of China's aerospace sector. Guided by the requirements for building a strong aerospace nation, this paper focuses on advancing the high-quality development of China's aerospace remote sensing. It systematically reviews the current development status, major achievements, and challenges confronted by China's aerospace remote sensing, conducts an in-depth analysis of the development models and characteristics of international aerospace remote sensing, and on this basis, explores new ideas and models for the construction of China's satellite remote sensing system, with a view to providing references for promoting the high-quality development of China's aerospace remote sensing.
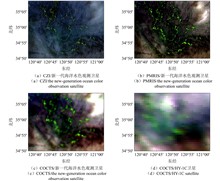
In recent years, the green tide of Enteromorpha prolifera has become a marine ecological disaster in the Yellow Sea. Meanwhile, as a technology, the satellite remote sensing provides effective basic monitoring information for the prevention and control of the marine ecological disaster. The China's Ocean Color Satellites (HY-1C, HY-1D and the new-generation ocean color observation satellite) can provide multi-resolution synchronous observation data for monitoring the large floating Enteromorpha prolifera. In this study, the analysis method of quasi-true color synthesis for image and the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) are used to analyze the remote sensing characteristics of floating Enteromorpha prolifera on the sea surface from the image, spectrum, spatial-temporal coverage and the difference of the extracted information by using the multi-resolution remote sensing monitoring data. The analysis results indicate: spatial resolution is the key influencing factor for remote sensing monitoring of floating seaweed on the sea surface; China's ocean color satellite remote sensing images with spatial resolution of higher than 500 m can be well used for monitoring the floating Enteromorpha prolifera in its outbreak period; China's ocean color satellites can cover the floating Enteromorpha prolifera monitoring area in the Yellow Sea once a day with the medium resolution; NDVI increases with the enlargement of the seaweed's coverage; the distribution of Enteromorpha prolifera directly observed from remote sensing images with different resolutions has significant differences, and there is a negative correlation between their resolution and the monitored distribution area. The results of the paper have significance in ecological monitoring applications by using China's ocean color satellite data and demonstrating the specifications for coming satellite.